Taxonomy
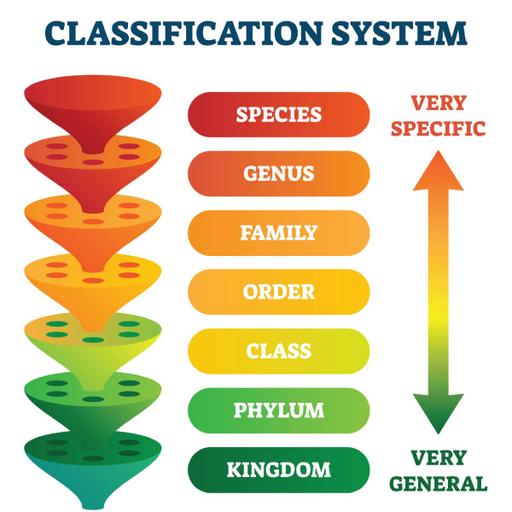
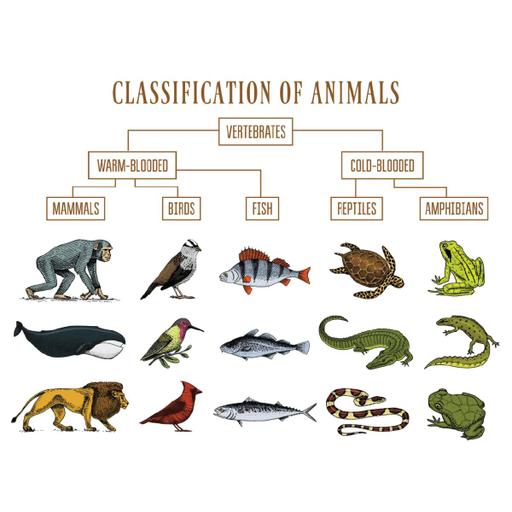
Taxonomy is the science of naming, describing and classifying organisms and includes all plants, animals and microorganisms of the world. There are eight distinct taxonomic categories. These are: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species. The three domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryota. A taxonomic characteristic may be defined as any expressed attribute of an organism that can be evaluated and that has two or more discontinuous states or conditions. The taxonomic value of a characteristic is increased if the biological significance of the characteristic has been determined. In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature (two-term naming system) or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms. It is the practice of identifying different organisms, classifying them into categories and naming them. All organisms, both living and extinct, are classified into distinct groups with other similar organisms and given a scientific name. The classification of organisms has various hierarchical categories.