Classification of Living Organisms
Presentations | English
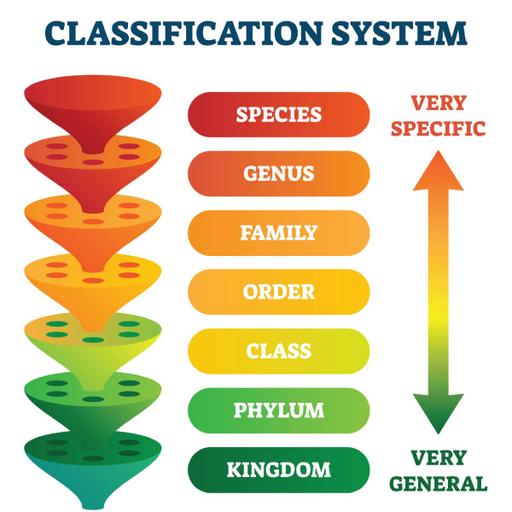
The classification of all living entities is based on extremely basic, universal traits. Each group's organisms are subsequently subdivided into smaller groupings. Each bigger group is divided into smaller groups based on more detailed commonalities. Scientists can examine certain groupings of organisms more easily thanks to this classification scheme. Living organisms are classified based on characteristics such as appearance, reproduction, mobility, and functionality, to name a few. The classification of living things refers to all of these specialised categories. Kingdom, phylum, classes, order, family, genus, and species are the seven levels of classification for living organisms. Kingdoms are the most fundamental division of living beings. There are five kingdoms in existence at the moment. Living organisms are classified into kingdoms based on how they get their nourishment, the sorts of cells that make up their bodies, and the total amount of cells in their bodies. In the categorization of living things, the phylum is the next step beyond kingdom. It's an attempt to discover physical commonalities between creatures within a kingdom. These morphological similarities show that creatures in a certain phylum share a common ancestor. A phylum's organisms are further divided into classes. A class of organisms has even more in common than an entire phylum. Each class of organisms is further divided into orders. An organism's taxonomic order is determined using a taxonomic key. A taxonomy key is essentially a collection of traits that governs how organisms are classified. Families are made up of orders. Species from the same family have more in common than organisms from higher classification levels. Organisms belonging to the same family are said to be related since they have so much in common. The Hominidae family includes humans. A genus is a term used to describe an organism's generic name. Because each genus is relatively specialised, there are fewer creatures in each one. As a result, both animals and plants have a large number of diverse genera. The genus is used to determine the first component of an organism's two-part name when employing taxonomy. Species are as distinct as they come. It is the most basic and stringent classification system for living things. The ability to breed with other organisms of the same species is the most important requirement for placing an organism in a certain species. The second part of an organism's two-part name is determined by its species.
51.00
Lumens
PPTX (102 Slides)
Classification of Living Organisms
Presentations | English
