Structure, Types & Function of Neurons
Presentations | English
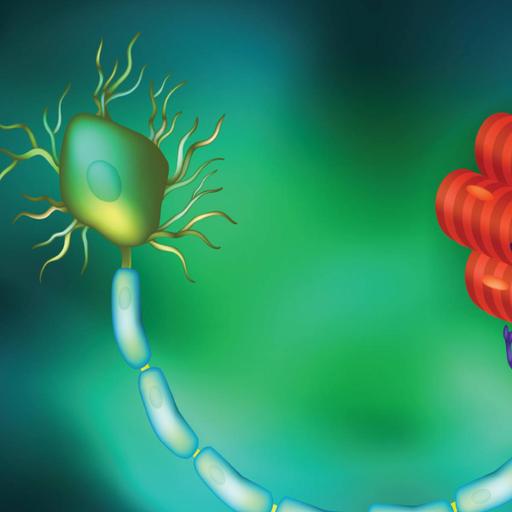
Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals throughout the body. Neurons have long extensions that extend out from the cell body called dendrites and axons. Dendrites are extensions of neurons that receive signals and conduct them toward the cell body. Neurons (also called neurons or nerve cells) are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for receiving sensory input from the external world, for sending motor commands to our muscles, and for transforming and relaying the electrical signals at every step in between. All neurons obtain a soma, containing the same organelles found in all animal cells. These organelles, however, vary in amount within the soma of a neuron compared to other cells as a reflection of the cell’s specific functions. For instance, the volume of rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons is richer than glia and other non-neuronal cells. Also present within the soma is cytosol a salty potassium rich fluid within the soma separated from the outside by the neuronal membrane its role shall be briefly be explored farther on.
10.25
Lumens
PPTX (41 Slides)
Structure, Types & Function of Neurons
Presentations | English
