MITOSIS
Presentations | English
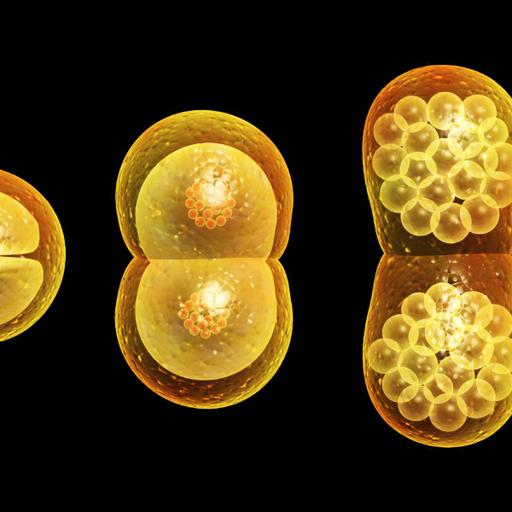
Why is Mitosis important in cell biology? Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells (cell division). During mitosis one cell divides once to form two identical cells. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells. Mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The result of mitosis is two identical daughter cells, genetically identical to the original cell, all having 2N chromosomes. The end result of mitosis is growth of the eukaryotic organism and replacement of some eukaryotic cells. After fertilization, growth occurs by cell division through mitosis into the 2-cell stage, then the 4-cell stage, 8-cell stage, 16-cell stage, and so on.
Free
PPTX (18 Slides)
MITOSIS
Presentations | English
