Krebs Cycle
Presentations | English
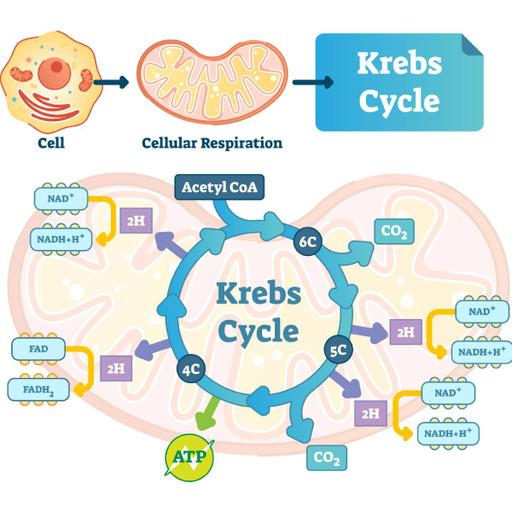
The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions which occur in the mitochondria and results in the formation of ATP and other molecules which undergo farther reactions to form more ATP. Cellular respiration can be divided into four sequences. The first sequence is glycolysis, its breaks down one molecule glucose into two molecules pyruvate. Transition takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and it’s referred to the beginning of aerobic respiration. The process takes place if there is enough amounts of oxygen in the mitochondria. However if there is insufficient oxygen in the mitochondria it could result into fermentation. The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration. The cycle harnesses the available chemical energy of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) into the reducing power of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).
12.50
Lumens
PPTX (50 Slides)
Krebs Cycle
Presentations | English
