Ionic Bonding
Presentations | English
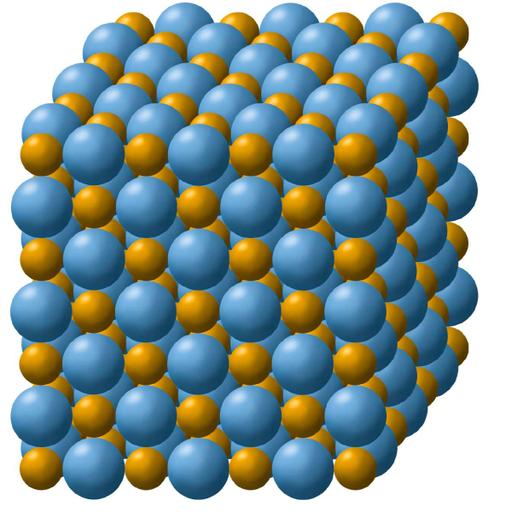
Relationships formed by covalent bond is less vulnerable than ionic bond! Chemistry is the study of elements and the different species (compounds, ions, complexes, and so on) that these elements produce. Thus, it is critical to comprehend how atoms in molecules are kept together, what forces hold these atoms together, and what variables are responsible for various molecule orientations. When two oppositely charged ions come together, they form an electrostatic (coulombic) connection. When atoms of a low-ionization-energy element give up part of their electrons to establish a stable electron configuration, ionic bonding results. Cations are created as a result of this process. When an atom of a different element with a higher electron affinity accepts one or more electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, the atom transforms into an anion. Typically, ionic substances do not conduct electricity when solid, but do when melted or in solution. The charge of the ions in ionic compounds determines their melting point. The greater the cohesive forces and the higher the melting point are in direct proportion to the charge. Their water solubility decreases with increasing cohesive force; thus, less water dissolves them.
15.00
Lumens
PPTX (30 Slides)
Ionic Bonding
Presentations | English
