Distributed Database
Presentations | English
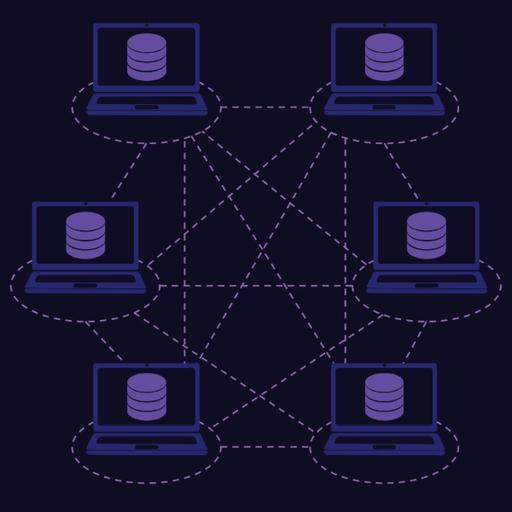
A distributed Database management system (DBMS) is a type of database that regulates storage devices connected to multiple CPUs. There are cases where multiple computers are located in one spot or allocated over a group of computers connected to a computer network. Data collection in a database can be distributed and stored in many physical locations. A network server with a distributed database may be connected to the Internet, in the case of one company's intranet or extranet, which may be on another company's network. Database duplication and distribution improve the performance of the database from the user's point of view. The contents of the distributed database are copied and pasted to guarantee that the latest updates are received. Mirroring uses special software that mirrors data updates in a distributed database. If an update is found, the copy method adds the same update to all database groups. The copying method can be very complex and time-consuming depending on the size of the distributed database or the number of blocks distributed. On the other hand, copying is not that complicated. One database is copied to the primary and the other to the database. Normal copying seizes place over many hours at a provided time. This assures that each location data distributed is the same. Users can access the distributed database as follows: Local applications, Applications that do not request data from other sites, Global application Applications that request data from other sites. The distributed Database does not share the main memory and disk.
13.50
Lumens
PPTX (54 Slides)
Distributed Database
Presentations | English
