Cell Division
Presentations | English
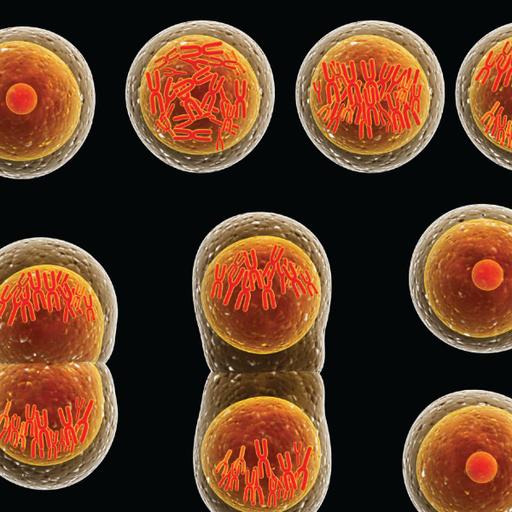
What is cell division defined as? It is the process by which cells multiply involving both nuclear and cytoplasmic division: both meiosis and mitosis. These phases are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis. The first step of cell division is prophase, during which the nucleus dissolves and the chromosomes begin migration to the midline of the cell. The interphase cycle accounts for about 90% of the cell cycle. This phase is where the cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division. Usually, cells will take between 5 and 6 hours to complete S phase. G2 is shorter, lasting only 3 to 4 hours in most cells. In sum, then, interphase generally takes between 18 and 20 hours. Mitosis, during which the cell makes preparations for and completes cell division only takes about 2 hours.
13.00
Lumens
PPTX (52 Slides)
Cell Division
Presentations | English
