Cardiovascular System
Presentations | English
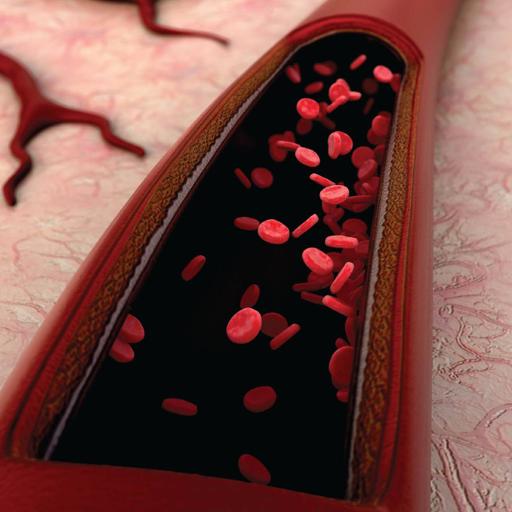
The cardiovascular system is sometimes called the blood-vascular, or simply the circulatory, system. It consists of the heart, which is a muscular pumping device, and a closed system of vessels called arteries, veins and capillaries. The cells of the cardiovascular system include endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, lymphatic endothelial cells, cardiomyocytes and atherosclerosis cells. Each of these cells plays a critical role in circulating, maintaining, and supporting cardiovascular activity, perfusion and system development. The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide. The main artery of the systemic circulation is the aorta. It is attached to the left ventricle of the heart and carries oxygenated blood. You can feel your pulse in an artery such as the carotid artery in the neck or the radial artery in the wrist.
7.25
Lumens
PPTX (29 Slides)
Cardiovascular System
Presentations | English
